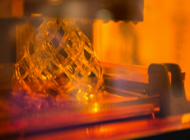
From a historical point of view, SLA is considered to be the process behind 3D printing. The first 3D printing patented application was file by Chuck Hill in 1984.
SLA or Stereolithography is one of the commonly used 3D printing technologies. It allows engineers and designers to produce 3D plastic parts with high accuracy and high resolution, fine details and smooth surface finish.
To learn more about this 3D printing technology, here are 4 vital aspects that help understand SLA(Stereolithography) better.
What is SLA (Stereolithography)
SLA uses a laser to cure photopolymer resin layer by layer. In this method, the laser or light solidifies liquid resin through a process called photopolymerization.
SLA 3D printers use liquid printing material and UV protection cover. SLA printers usually offer a relatively small volume of production compared to other 3D printing technologies. However, there are other SLA 3D printers that can produce larger parts.
A standard SLA 3D printer is composed of 4 primary sections:
- A tank filled with liquid photopolymer or liquid resin which is usually clear liquid plastic
- A perforated platform that is immersed in a tank and can be moved up and down according to the printing process
- High-powered ultraviolet laser
- A computer interface that manages the platform and laser movements
Benefits and limitations of SLA
One of the advantages of using SLA is that it can produce very high dimensional and accurate 3D parts. It can also produce parts that have very smooth surface finish which is ideal for visual prototypes.
On the other hand, parts that are printed with SLA can be brittle and may not be suitable for functional prototypes. 3D parts that are produced via SLA tend to curl or warp. Moreover, its mechanical properties and visual appearance may degrade over time especially when exposed to sunlight.
SLA 3D printing workflow
SLA has two main types: laser-based (or simply SLA) and projection-based (DLP or Digital Light Projection). Both have an similar procedure but uses different light sources. SLA uses a laser while DLP uses a projector.
To understand it better, this is how SLA 3D printing works:
- The build platform is positioned in a tank of liquid photopolymer. It should have a distance of one layer height for the surface of the liquid.
- To start, the UV laser creates each layer by selectively curing and solidifying photopolymer resin.
- When a layer is finished, the platform will move at a safe distance and a sweeper blade recoats the surface. This process is repeated until the part is completely finished.
- After printing, the 3D part may require further post-processing procedure.
Overview of SLA materials
SLA can produce 3D parts from thermoset polymers or resins through the process of photopolymerization. Here is an overview of the common SLA materials.
- Standard resin
Standard resins have high tensile strength but are known to be very brittle. This means that it is not suitable to use for functional parts. Since it has the ability to create fine features, it is also ideal for making visual prototypes and art models.
- Clear resin
Clear resins are basically transparent material that is used for SLA 3D printing. It has similar mechanical properties to standard resin and can be post-processed to near optical transparency. Clear resins are often used for showcasing internal features, LEDs housing and fluidic devices.
- Castable resin
This type of resin is ideal for making jewellery and other small and intricate components. This material enables parts to be printed with sharp details and smooth finish. It will also burn out easily and will not leave any ashes or residue.
- Tough or durable resin
It is called durable resin as it has the highest impact strength and elongation at break among other SLA materials. It is usually used for prototyping parts with moving elements and snap-fits.
- Heat-resistant resin
This resin is ideal for application that requires high thermal stability. This material has a heat deflection temperature between 200-300ᵒC. It is typically used for manufacturing heat-resistant fixtures, hot air and fluid flow equipment, casting and thermoforming tooling and mould prototypes.
- Dental resin
Dental long term Biocompatible resin (Class IIa biocompatible) is a special type of resin that is designed for long term orthodontic purposes. This resin can be in contact with human body for as long as one year.
Conclusion
SLA is best suited for engineers and designers who need to produce small, smooth parts with fine details and high level of accuracy.
In this blog post, you have learned about how SLA 3D printing works, advantages and limitations, common SLA materials and other aspects in SLA 3D printing.
For those who are interested in SLA 3D printing, you can ask for professionals or approach a 3D printing service provider. They can give you advices regarding SLA 3D printing and provide services related to 3D printing.








